The pharmaceutical industry's transition toward recombinant cascade reagents (rCR) for bacterial endotoxins testing (BET) represents a significant advancement in sustainability and reliability. However, comprehensive validation across diverse endotoxin serotypes and testing platforms remains essential for widespread adoption.
In collaboration with ACC, we conducted a comparative study examining the performance characteristics of microfluidic and traditional plate-based detection methods using recombinant reagents. This research, presented at the PDA Pharmaceutical Microbiology Conference, demonstrates equivalent performance of these platforms in detecting various bacterial endotoxin serotypes, including naturally occurring endotoxins, from multiple Gram-negative bacterial sources.

Our findings provide critical validation data supporting the use of rCR technology with an advanced microfluidic platform, addressing key questions regarding serotype recovery, platform comparability, and analytical performance. Results confirm that recombinant cascade reagents achieve effective recovery and reliability across diverse endotoxins, further validating their suitability as a robust alternative to traditional Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) reagents for endotoxin testing.
Background: rCR Technology and Endotoxin Detection Methods
Recombinant Cascade Reagents (rCR) represent a sustainable alternative to traditional LAL for bacterial endotoxin testing. By leveraging recombinant technology, rCR replicates the full LAL cascade without relying on horseshoe crab-derived resources, aligning with industry sustainability goals. As adoption of rCR expands, comprehensive validation across naturally occurring endotoxins from diverse Gram-negative bacterial sources becomes increasingly critical.
This study evaluates PyroSmart NextGen® rCR performance across lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from multiple Gram-negative bacterial species using three independent commercial lots. Additionally, the investigation compares two detection platforms - the Sievers Eclipse BET Platform and traditional 96-well microplates - to assess consistency of endotoxin recovery across serotypes and evaluate each platform's performance characteristics.
Study Design: Comparison of Modern Microfluidic Platforms to Traditional Bacterial Endotoxin Testing
Study objectives:
- Evaluate recovery of diverse endotoxin serotypes using ACC's PyroSmart NextGen® rCR on both the Sievers Eclipse BET Platform and 96-well microplates with Molecular Devices SpectraMax® reader
- Assess platform comparability between microfluidic and traditional 96-well microplate-based detection methods
- Characterize performance parameters across multiple LPS sources
Test materials:
- LPS solutions created from Gram-negative microorganism strains (Microbiologics KWIK-STIKs)
- Reference Standard Endotoxin (RSE) lot R172R0
- PyroSmart NextGen® rCR (ACC)
Methods:
Crude lipopolysaccharide (LPS) solutions were prepared from monocultures of the following Gram-negative microorganisms:
- B. cepacia, derived from ATCC® 25416™
- E. coli, derived from ATCC® 8739™
- P. aeruginosa, derived from ATCC® 10145™
- R. pickettii, derived from ATCC® 27511™
- S. enterica, derived from ATCC® 51741™
- S. maltophilia, derived from ATCC® 13636™
Cultures were suspended in Water for Cell Culture (WFCC), heated, vortexed, and filtered through 0.2µM syringe filters. Solutions were diluted to achieve target responses of 0.5-1.0 EU/mL. Tap water was also collected and diluted to the same target EU/mL.
As a control for the LPS extraction method, WFCC was heated, vortexed, and filtered via the same methodology and tested for interference and contamination. The WFCC control demonstrated equivalent performance characteristics as LAL Reagent Water (LRW) in assays.
Reference Standard Endotoxin (RSE, lot R172R0) was prepared across a concentration range of 50-0.005 EU/mL via serial dilution and tested as a standard curve contemporaneously alongside all samples.
Results and Conclusions:
BET Platform Equivalency and Performance Characteristics of rCR
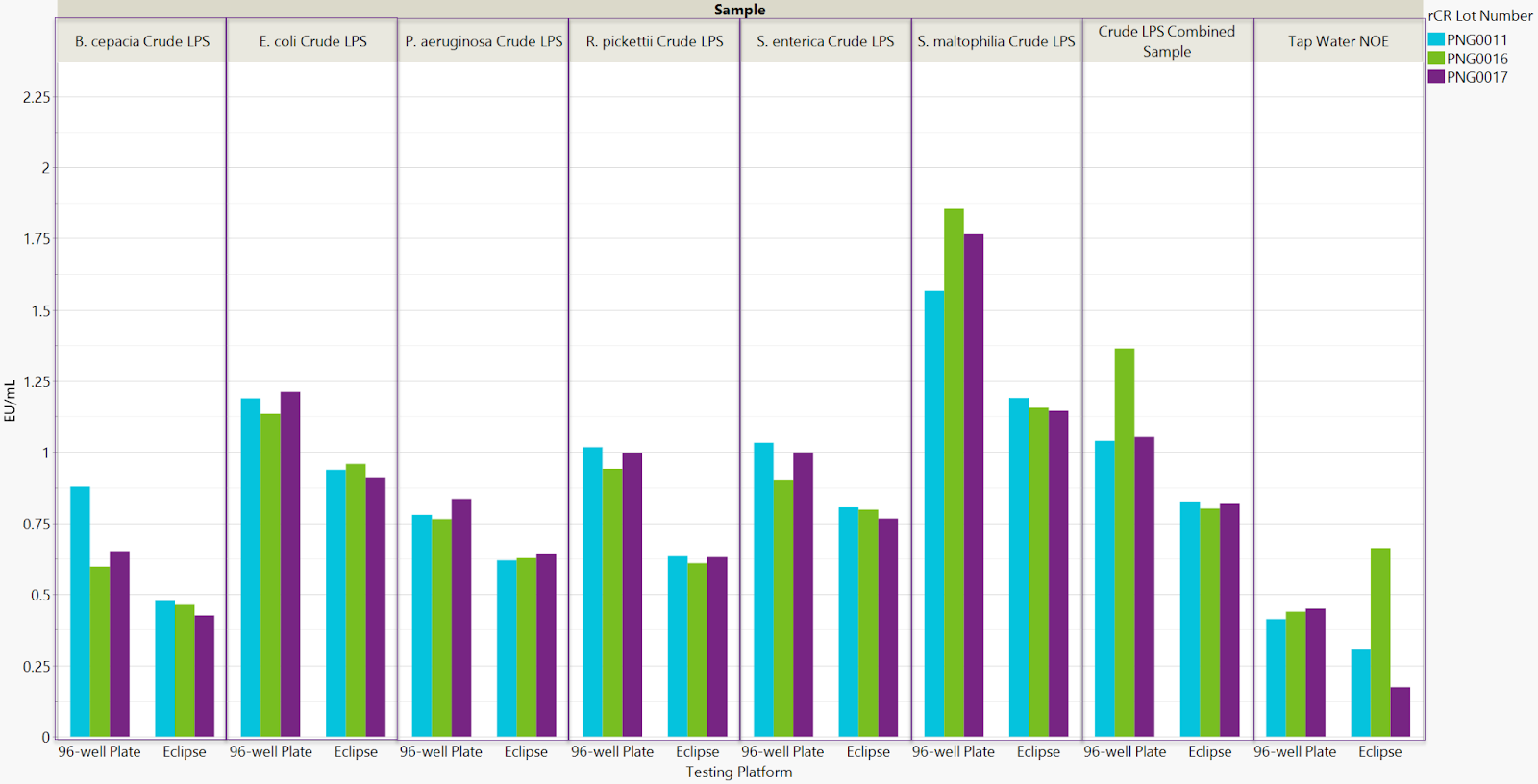
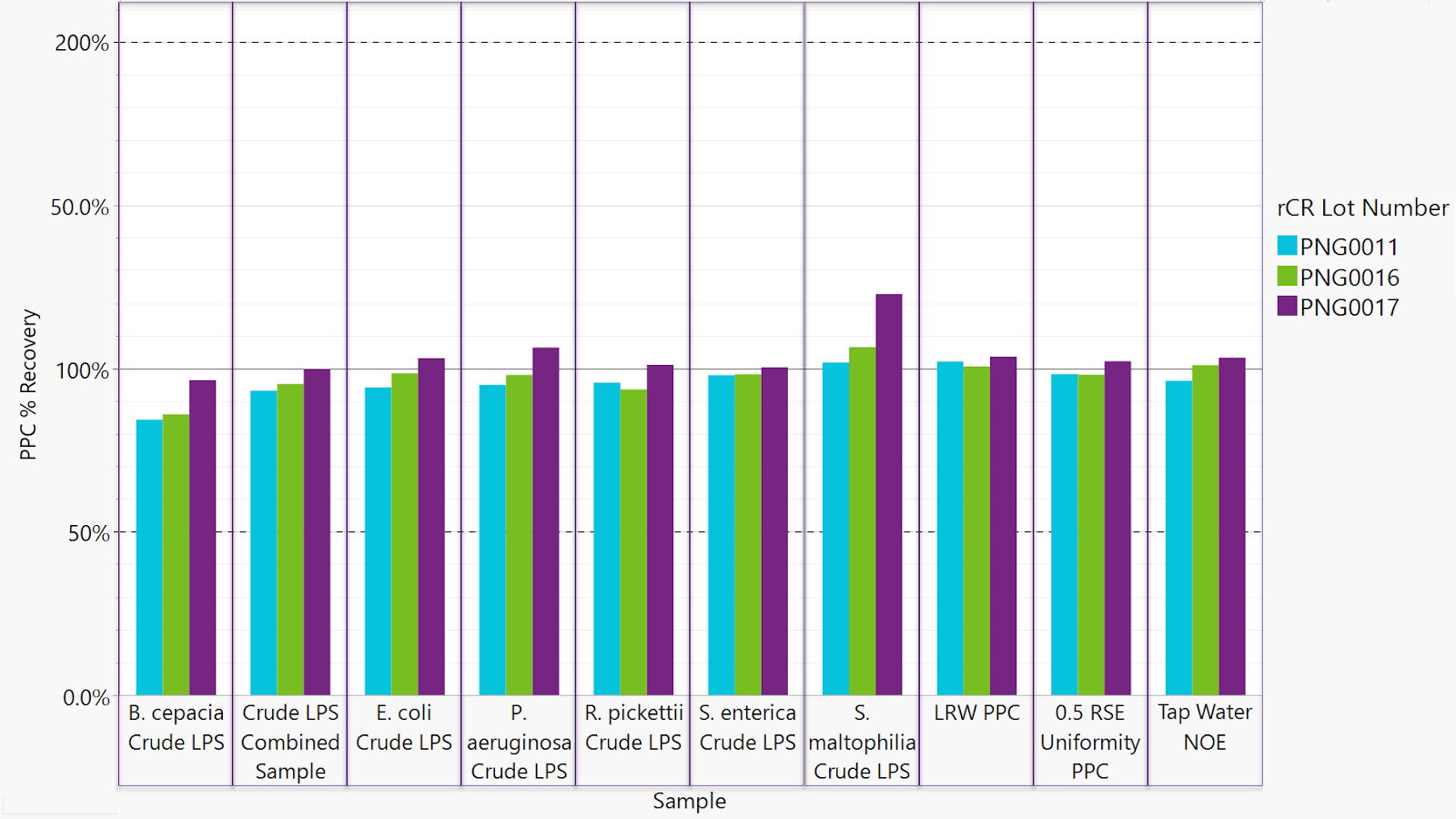
This investigation confirms equivalent performance between the Sievers Eclipse BET Platform and traditional 96-well plate methodology in detecting various bacterial endotoxin serotypes, including naturally occurring endotoxins. Data validate the Eclipse platform's effective use of recombinant cascade reagents (rCR) for reliable recovery across diverse endotoxins.
The Eclipse's centripetal microfluidic technology provides operational advantages, including reduced assay time and decreased potential for errors. At a sensitivity of 0.005 EU/mL, the average reaction time for RSE on the Eclipse was 1,692 seconds, representing a 37% reduction compared to 2,687 seconds observed with the SpectraMax.
Key findings support the Eclipse platform as a compliant solution for endotoxin testing, offering:
- Enhanced analytical efficiency with significant time savings
- Decreased variability through automated microfluidic processing
- Sustainable testing practices via rCR compatibility
- Maintained sensitivity and accuracy across diverse endotoxin sources
These results contribute to the growing body of evidence supporting rCR adoption and advanced microfluidic platforms for pharmaceutical quality control applications.
En savoir plus sur le Sievers Eclipse
Authors:
- Veronika Wills
-
Veronika Wills directs Global Technical Service groups at Associates of Cape Cod, Inc. She joined the team in 2007 and has since become a globally recognized subject matter expert and public speaker on endotoxin and glucan testing. She brings an in-depth expertise that is vital to ACC customers when it comes to technical support of testing complex sample matrixes, troubleshooting, method validations, investigations and regulatory aspects of BET. Most recently, Veronika has been heavily involved in the assessment and implementation of recombinant technologies and their automation. Veronika holds a Master’s Degree in Biochemical Engineering from the Institute of Chemical Technology in Prague, Czech Republic.
- Meg Provenzano
-
Meg Provenzano is the Global Product Manager for Sievers endotoxin instruments at Veolia. Elle possède plus de 10 ans d'expérience dans le secteur des tests d'endotoxines bactériennes et a occupé plusieurs postes liés au contrôle de la qualité, à l'assistance technique et à la gestion des produits. Avant de rejoindre Veolia, Meg était chef de produit chez Charles River Laboratories. Elle est attentive aux besoins des clients et aime résoudre les problèmes sur le terrain, qu’il s’agisse de questions techniques, d’aide à l’analyse ou de logiciels. Meg est titulaire d'une licence en sciences et biologie marines de l'université de Coastal Carolina, où elle s'est spécialisée sur la recherche concernant les populations de dauphins.
- Jake Vincent
-
Jake Vincent is the Biodetection Specialist and Advanced Lead Researcher for the Sievers R&D group at Veolia, specializing in the development of biodetection analytical instrumentation. A key contributor to the Sievers Eclipse Endotoxin Analyzer, Jake was responsible for designing the predeposited standards featured in the microfluidic consumable device. Jake’s research on microfluidic endotoxin detection, "Miniaturization, Parallelization, and Automation of Endotoxin Detection by Centrifugal Microfluidics," has been co-authored and published in Analytical Chemistry. Prior to joining Veolia, Jake contributed to analytical method development for flavivirus vaccine testing at Inviragen and Takeda Vaccines, including clinical trial testing for the dengue vaccine, Qdenga. He holds a B.S. from Colorado State University.
